What is chickenpox?
Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus. It is most common in children. Most cases occur in people who are younger than 15 years of age. Chickenpox is usually a mild illness. The most common symptom is itchy red dots that appear over the entire body. The dots turn into fluid-filled blisters and end as scabs. The disease can also cause flu-like symptoms, including fever, drowsiness, poor appetite, headache, and sore throat. Some children get sicker than others.
Chickenpox can be a very serious illness in infants and adults. It can be especially serious if you are pregnant or have a compromised immune system. Chickenpox can cause problems such as skin infections, brain swelling, and pneumonia. Because it is so contagious, a child who has chickenpox shouldn’t go to school or day care until all the sores have dried or crusted. Many parents miss work during the time their child has chickenpox.
Path to Improved Health
Chickenpox was once a common childhood disease until a vaccine was invented to prevent it. Today, you can keep your children from getting chickenpox by making sure they get the vaccine.
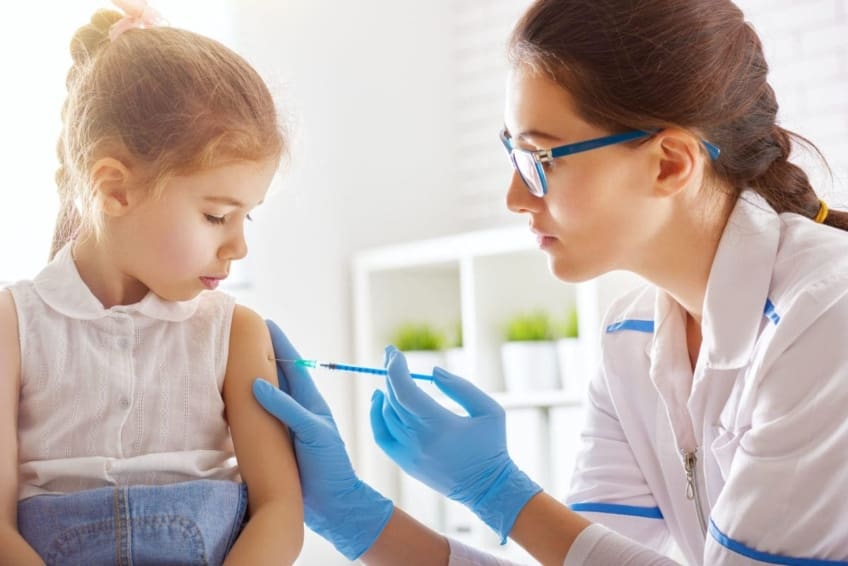
The purpose of a vaccine is to prevent you from getting a specific disease. The chickenpox vaccine is called the varicella vaccine. Varicella is the name of the virus that causes the disease. It is given by injection (shot). More than 90% of people who receive the vaccine will not get chickenpox. People who get chickenpox after having the vaccine usually don’t get as sick.
Who should be vaccinated against chickenpox?
The chickenpox vaccine is given in 2 doses. The first dose is given when your child is 12 to 15 months old. The second is given when he or she is between 4 and 6 years of age. It can also be given to older children and adults at any time. Anyone who has not had chickenpox should get the vaccine. It is especially important for:
- Health care or daycare workers
- Teachers
- College students
- Military personnel
- Inmates and staff of correctional institutions
- Women of childbearing age who are not pregnant (women should avoid pregnancy for 1 month following the vaccine)
Things to Consider
Not everyone should get the chickenpox vaccine. Those who shouldn’t include:
- Anyone who has a serious illness
- Pregnant women
- Anyone who has had a serious allergic reaction to the varicella vaccine in the past
You should talk to your doctor before getting the vaccine if you:
- Have an immune system disease, such as HIV.
- Are receiving high doses of steroids, such as prednisone.
- Are receiving treatment for cancer with radiation, drugs, or chemotherapy.
- Have recently received blood products, such as a blood transfusion.
Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about whether you should receive the chickenpox vaccine.
Are there any side effects from the vaccine?
Most kids have no problems with the chickenpox vaccine. The most common side effects are pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site. Severe reactions are rare. If your child seems to be having a reaction to the vaccine, call your doctor. Call 911 or go to the hospital if your child:
- Gets hives (bumps, swelling, itching, or burning on their skin)
- Has trouble breathing
- Goes into shock (becomes weak, cold, damp, or sweaty)
- Loses consciousness
Tell the doctor the day and time your child was given the vaccine. You should also file a Vaccine Adverse Event Report form with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Ask the doctor to do this, or you can call 800-822-7967.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- Why does my child need the chickenpox vaccine?
- What could happen if I don’t get my child vaccinated?
- When should I schedule each dose of the vaccine?
- Should older children or adults get the chickenpox vaccine?
Resources
Centers for Disease Control: Chickenpox Vaccination
National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: Chickenpox Vaccine
![]()
Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians
This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.