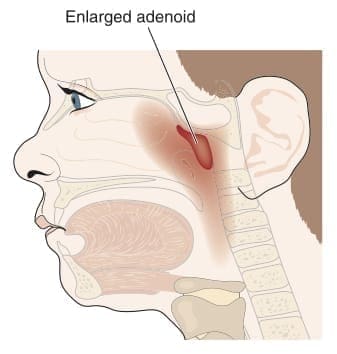
What are enlarged adenoids?
Adenoids are tiny pieces of tissue in the back of your throat. They hang above your tonsils.
Adenoids help fight infections in your body. They are the most helpful between birth and age 5. They catch the germs that make you sick. That’s what causes them to increase in size. They return to normal size when you are healthy.
After age 5, adenoids shrink in size. They no longer play a big role in your body’s health. It is not normal for them to remain swollen (enlarged). However, if they do, you need to see your doctor. This rarely happens as an adult.
Symptoms of enlarged adenoids
If you have enlarged adenoids, you may have these symptoms:
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Feeling like your ears are blocked
- Difficulty sleeping
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swollen neck glands
- Snoring
- Sleep apnea (a condition that causes you to stop breathing for short periods while sleeping)
- Chapped lips/bad breath (due to breathing through your mouth)
Causes
Infections cause them to temporarily increase in size.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will do a physical exam. They will look at the back of your throat. This may be done by inserting a thin, flexible scope with a mirror through your nose and down the back of your throat. This procedure may be uncomfortable but should not be painful.
Tell your doctor if you have a stuffy nose, sore throat, or your ears hurt. They may order a blood test to see if you have an infection. Your doctor may also order a sleep study to see if you have sleep apnea. This helps determine whether enlarged adenoids are the reason for your sleep problems.
Prevention
Having enlarged adenoids is a common condition for children. It is less of an issue as people age. There is nothing you can do to prevent it. Prompt attention for a sore throat or ear infection can help your doctor monitor their size. This may reduce your discomfort.
Treatment
Treatment depends on your age and how long your adenoids have been enlarged. Your doctor may monitor their size over time or prescribe medicines or a nasal spray to reduce swelling. Surgery to remove your adenoids and tonsils at the same time is common. This is common if you have frequent ear and throat infections, trouble breathing, or sleep apnea.
Living with enlarged adenoids
Children with enlarged adenoids are treated with an antibiotic. This is to eliminate the infection that is causing them to enlarge. Be sure your child takes the full dose. A partial dose will allow the infection to return. If medicine is not effective after repeated illness, your doctor may discuss surgery.
Questions to ask your doctor
- Can I have my child’s adenoids removed as an elective surgery?
- What is the recovery time for removal surgery?
- Does strep throat cause enlarged adenoids?
![]()
Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians
This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.