Follow this chart for more information about pain and swelling in your legs.
American Academy of Family Physicians.
American Academy of Family Physicians.
Leg Problems
Step 1
Selecting A Symptom
- Abdominal Pain (Stomach Pain), Long-term
- Abdominal Pain (Stomach Pain), Short-term
- Ankle Problems
- Breast Problems in Men
- Breast Problems in Women
- Chest Pain in Infants and Children
- Chest Pain, Acute
- Chest Pain, Chronic
- Cold and Flu
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Ear Problems
- Elimination Problems or Constipation
- Elimination Problems or Constipation in Infants and Children
- Eye Problems
- Facial Swelling
- Feeding Problems in Infants and Children
- Fever
- Fever in Infants and Children
- Foot Problems
- Genital Problems in Infants (Female)
- Genital Problems in Infants (Male)
- Genital Problems in Men
- Genital Problems in Women
- Hair Loss
- Hand/Wrist/Arm Problems
- Headaches
- Hearing Problems
- Hip Problems
- Knee Problems
- Leg Problems
- Lower Back Pain
- Menstrual Cycle Problems
- Mouth Problems
- Mouth Problems in Infants and Children
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Nausea and Vomiting in Infants and Children
- Neck Pain
- Neck Swelling
- Shortness of Breath
- Shortness of Breath in Infants and Children
- Shoulder Problems
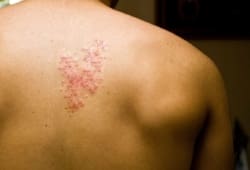
- Skin Rashes & Other Skin Problems
- Throat Problems
- Tooth Problems
- Urination Problems
Step 2
Answering Questions
Do you have pain in your leg or ankle after a fall or injury?
Is there a deformity of your leg, or are you unable to stand or put pressure on your leg?
Did you hear a popping or grinding sound at the time of the injury?
Is there bruising or swelling of your calf or ankle?
Do you have pain or mild swelling in the front or inner part of your lower leg that may have developed soon after starting or increasing physical activity, such as running, jumping or marching?
Do you have pain, swelling, redness, or warmth in your calf? Is one calf bigger than the other?
Do you have twisted dark blue or purple veins near the surface of the skin of your calf, and do you have pain or cramping in your calf or leg that is worse after standing or sitting for a long time?
Do you have a tender red area or a red streak anywhere on your leg?
Do your calves ache after walking, and is the pain relieved with rest?
Do you have swelling in both of your feet or lower legs?
Step 3
Possible Causes
Diagnosis
You may have BROKEN BONE, such as the TIBIA or FIBULA in the lower leg, or the FEMUR in the upper leg (especially if you aren’t able to bear any weight on your leg).
Self Care
EMERGENCY
See your doctor or go to the emergency room right away. Apply ice to the affected area.Diagnosis
You may have a SPRAINED ankle, but it’s possible to break a bone of the lower leg and still be able to stand on it. You also may have ruptured or tore a LIGAMENT in your knee or ankle.
Self Care
EMERGENCY
See your doctor or go to the emergency room right away, especially if your knee is swollen. Apply ice to the affected area.Diagnosis
You may have a partial or complete TEAR of the ACHILLES TENDON that attaches the calf muscle to the heel. This injury will cause pain and difficulty pointing the foot down or walking. A TORN CALF MUSCLE will cause pain with walking and might produce bruising.
Self Care
See your doctor as soon as possible. Apply ice and use an anti-inflammatory medicine, such as ibuprofen. Avoid activities that cause pain.
Diagnosis
A MUSCLE PULL or STRAIN will cause pain and stiffness in the calf muscle without any bruising or swelling.
Self Care
Apply ice and use an anti-inflammatory medicine. Avoid activities that cause pain.
Diagnosis
You may have SHIN SPLINTS, inflammation of the ligaments and other connective tissue along your TIBIA bone, or a STRESS FRACTURE, a tiny crack in the bone. These injuries are often caused by overuse during physical activity.
Self Care
Get plenty of rest and avoid activities that cause pain. Use an anti-inflammatory medicine such as ibuprofen and apply ice to the area. See your doctor if pain or swelling gets worse or doesn’t get better.
Diagnosis
You may have a DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS, a clot in the veins of the calf muscles, often caused by prolonged inactivity, injury, or an underlying blood clotting problem.
Self Care
EMERGENCY
See your doctor or go to the emergency room right away. A blood clot in the legs could break away and block an artery in the lungs (causing pulmonary embolism), or in the brain (causing a stroke).Diagnosis
You may have VARICOSE VEINS, swollen veins caused by weak valves and vein walls. A milder version of this is often called SPIDER VEINS.
Self Care
Wear support/compression stockings or hose. Alternate periods of standing with sitting. See your doctor if the varicose veins are very prominent, or if they become painful and red or the skin over top of them begins to thicken or change.
Diagnosis
You may have an infection, such as CELLULITIS (infection of the skin), LYMPHANGITIS (infection of the lymph channels leading to lymph nodes) or OSTEOMYELITIS (infection of the bone).
Self Care
Apply mild heat and an antibiotic ointment. Call your doctor if you have a fever or if the red areas or pain get worse or do not go away.
Diagnosis
The pain may be caused by CLAUDICATION caused by PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE (PAD), narrowing of the arteries that carry blood to your leg muscles.
Self Care
See your doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnosis
You may have EDEMA, a build-up of fluids that may be caused from CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE, ACUTE OR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE or blockage of blood returning to the heart.
Self Care
See your doctor as soon as possible. If you are experiencing shortness of breath associated with this swelling, have someone drive you to the closest emergency room or call an ambulance.
Self Care
For more information, please talk to your doctor. If you think the problem is serious, call your doctor right away.