What are hives?
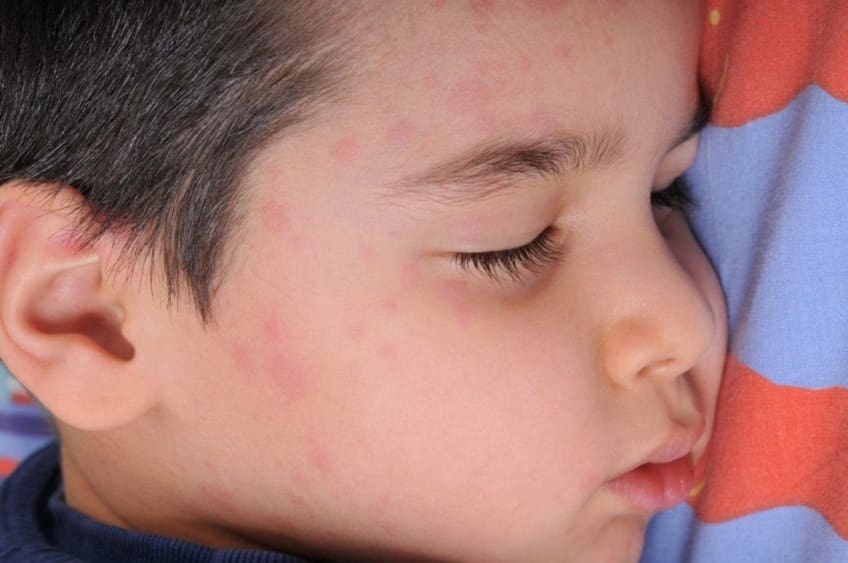
Hives are a skin condition. They are raised, red bumps on your skin. They can be itchy. Hives appear on the surface of your skin, not under your skin. The medical term for hives is urticaria. Sometimes they are called welts. Hives are common. You can get them at any age. You may get them once in your lifetime. You may get them repeatedly.
Hives symptoms and treatment
Common symptoms of hives
Hives can appear anywhere on your body. Common symptoms include the following:
- Red, raised bumps on your skin
- Itching
- A variety of shapes and size bumps
- Clear edges around the bumps
- The middle of the bump turns white when you press on it
- Bumps appear without warning
Over-the-counter and prescription treatments
Most cases of hives are harmless. They usually go away on their own. There are things you can do to lessen the discomfort. This includes:
- Take an antihistamine immediately. The over-the-counter medicine Benadryl will provide relief within an hour
- Avoid scratching the hives
- Apply an anti-itch cream
- Cover the area with a cold cloth
- Take a cook bath or shower. Take a hot bath or shower in cases of cold-induced hives
- Wear loose clothing
- Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and exercise (sweating irritates hives)
When to seek medical help
A severe case of hives may cause swelling in your throat, face, tongue or wheezing. This makes it difficult to breathe or swallow. Call 911 or go to the emergency room immediately. You may need a shot of epinephrine or steroids. This is a quick-acting treatment.
Causes and triggers of hives
Allergies and environmental factors
Most people get hives from an allergic reaction. Your body responds to allergies by releasing chemicals into your blood. These chemicals trigger the hives. Common causes include:
- Pollen
- Animal dander
- Insect bites
- Food, such as shellfish, fish, nuts, eggs, and milk
- Certain materials, such as wool or latex
- Extreme weather change
Stress, illness, and medications
Other causes include:
- Stress
- Hay fever
- Infection or illness
- Medicines
- Fatigue
- Tight clothing
- Quick change in body temperature
Vasculitis is a rare condition that causes painful hives. This is where your blood vessels inflame.
It’s difficult to know what triggered hives. It may be a guess based on the various causes.
How are hives diagnosed?
Your doctor will do a physical exam. He or she will look at the hives. Your doctor also may do a blood, skin, or urine tests. This can confirm if you had an allergic reaction and what caused it.
Can hives be prevented or avoided?
Hives cannot be prevented. If you know the various causes, try to avoid triggers. This includes:
- Avoiding food or materials you are allergic too
- Avoiding tight clothes for long periods
- Taking a break when you are stressed or overtired
- Washing your hands regularly
- Avoiding extreme temperature changes
Managing hives symptoms and treatment
If you’ve had hives once, you might be fearful that they will return. It’s helpful to have Benadryl handy, especially when traveling. If you have chronic hives (lasting longer than six weeks), see an allergist or dermatologist. These are doctors who specialize in allergies and skin conditions. Hives typically last a short time.
Questions to ask your doctor
- If I get hives, can I get them again?
- Are hives contagious?
- Can hives get infected if I scratch them?
- Could another medical condition be causing my hives?
Learn more about hives symptoms and treatment
![]()
Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians
This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.